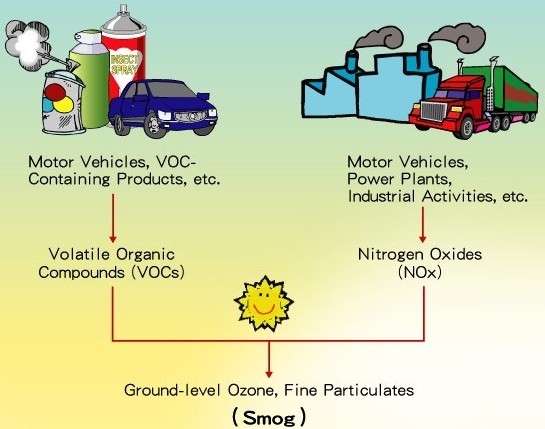
People frequently visualize the outside world, smog from automobiles and industries, or the clean air of the forests when they think about air quality. However, 90% of our waking hours are spent indoors, including at work, home, public places, and schools. One of the most crucial aspects of feeling at ease in a space is the indoor environment. Additionally, poor air quality can affect your productivity and possibly be harmful to your health. The least recognized are probably the volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
TVOCS has an impact on one’s comfort, well-being, and health.
Your sense of wellness and how comfortable you are within a building are both impacted by TVOCs. Even some VOCs are harmful to your health. More hazardous VOCs exist than others. A TVOC’s potential for harm also depends on variables including exposure dose and duration. Additionally, some people—particularly young children and the elderly—have higher levels of sensitivity than others. Some patients have reported immediate symptoms such as eye and respiratory tract irritation, headaches, dizziness, vision abnormalities, and memory impairment following exposure to VOCs. As an illustration, some people have an instant headache when they enter a freshly painted room. Some people might just find the smell repulsive.
TVOCs may lead to:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- irritated eyes, nose, and throat
- loss of coordination
- Fatigue
At typical levels, some VOCs (like toluene) can irritate the skin and trigger allergic reactions.
Unpleasant smells and stagnant air make people feel unclean and are unpleasant.
Formaldehyde is one of the VOCs that might cause cancer. Long-term exposure to VOCs in high quantities can harm the kidneys, neurological system, and liver.
Describe TVOC.
Describe TVOC. Total Volatile Organic Compounds, or TVOC. Organic substances known as volatile organic compounds are gases at room temperature. There are thousands of VOCs present, and numerous VOCs are present at once. To measure the concentration of all VOCs, the Total VOC is utilized the majority of the time. Compared to monitoring individual VOCs, this is simpler and less expensive.
VOCs include, for example:
- Benzene
- ethanol glycol
- Formaldehyde
- chloromethyl methylene
- Tetrachloroethylene
- Toluene
Where can you locate VOCs?
VOCs can come from a variety of sources, including you.
- Products
- Outside world
Products with VOC
Many VOCs originate from:
- sanitizers and cleaners
- Pesticides
- odor removers
- solvents and paints
- Glue
- fresh carpeting and furniture
- materials for construction
- electronic apparatuses
- Plywood
Therefore, certain VOCs may be present in everyday life, particularly in sprays and aerosols from cleaners and other products. Additionally, renovations and new construction could have a negative impact on health. New furniture, carpets, plywood, and construction materials all have the potential to raise indoor VOC concentrations owing to off-gassing. These new items pose major risks to your health up until the off-gassing has subsided. You can pollute on your own, but this is frequently much less destructive than what products do.
VOCs in the environment
Poor interior air quality can also be a result of industrial pollutants and vehicle emissions when the building’s windows are left open or the air conditioning system is malfunctioning. especially when the structure is located in a busy or industrial location.
Are VOCs generally harmful?
No matter whether the residences were in rural or heavily industrialized locations, the EPA’s Total Exposure Assessment Methodology (TEAM) investigations indicated that the levels of roughly a dozen common organic contaminants were 2 to 5 times greater inside homes than outside. Additional TEAM investigations show that humans can expose themselves and others to extremely high pollutant levels while using goods containing organic compounds, and that elevated amounts can linger in the air for a very long time after the activity is over.
(What are volatile organic compounds (VOCs)?, EPA, https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/what-are-volatile-organic-compounds-vocs)
TVOC concentrations can be calculated in milligrams per cubic meter (mg/m3), parts per million (ppm), or parts per billion (ppb) of air. According to the data below, TVOC concentrations of less than 0.3 mg/m3 are regarded as low values. Also permissible ranges are from 0.3 mg/m3 to 0.5 mg/m3.
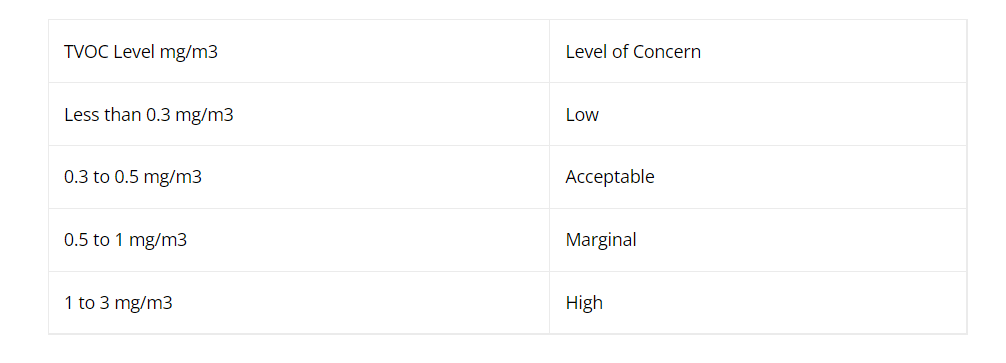
TVOC Level mg/m3 and Level of Concern
To ensure a safe and comfortable indoor air quality, Use GZAIR PT02 to measure the TVOC in your building.


Leave A Comment